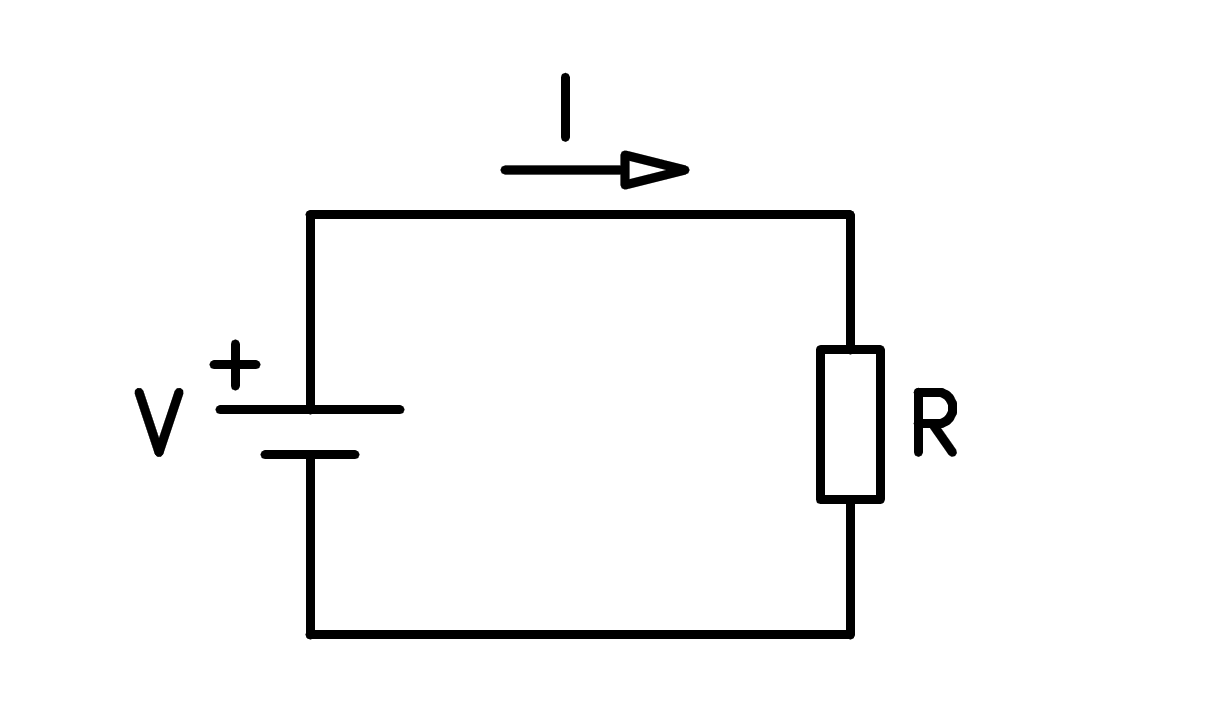
9. Ohm's law¶
Ohm's law establishes the relationship between the three main magnitudes of an electrical circuit with resistance.
- The greater the voltage, the greater the circuit current.
- The higher the resistance, the lower the circuit current.
Ohm law formula¶
Ohm's law expressed in a mathematical way has the following formula:
The magnitudes and units being the following:
I = current intensity in amperes [A]
V = Electrical voltage in volts [V]
R = Electrical resistance in Ohms [Ω]
Voltage variation¶
In the following simulation we will change the tension of the circuit to verify how it behaves. Changing the stack voltage from 5 volts to 15 volts (three times more), we can check how the current changes increasing up to three times more its initial value:
| Voltage [V] | Intensity [A] |
|---|---|
| 5 volts | 0.1 amps |
| 10 volts | 0.2 amps |
| 15 volts | 0.3 amps |
Exercise: add one more circuit to the simulation by copying and pasting one of the existing circuits and changing the stress value value so that the current is worth 0.5 amps.
Resistance variation¶
In the following simulation we will change the resistance of the circuit to verify how it behaves. Changing the resistor value from 10 ohms to 50 ohms, we can check how the current changes from its initial value to five times less:
| Resistance [Ω] | Intensity [A] |
|---|---|
| 10 ohms | 1 amperio |
| 20 ohms | 0.5 amps |
| 50 ohms | 0.2 amps |
Exercise: add one more circuit to the simulation by copying and pasting one of the existing circuits and changing the resistance value so that the current is worth 0.1 amps.
Exercises¶
What is Ohm's law? What type of circuits does it apply?
What is the formula of OHM's law and what are its magnitudes and units?
What happens to a circuit with resistance if we increase the tension?
What happens to a circuit with resistance if we increase the value of the resistance?
How much will the current intensity be worth in the following circuits?
Voltage [V] Resistance [Ω] Intensity [A] 20 volts 50 ohms 5 volts 1000 ohms 230 volts 10 ohms 3 volts 200 ohms